What is the sectoral carbon footprint?
The sectoral carbon footprint measures the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions generated by each economic sector, such as energy, transportation, industry, agriculture, and buildings. Each sector contributes differently to climate change based on its sources of emissions. Analyzing the carbon footprint by sector helps identify the most polluting activities and define specific strategies to reduce them.
Carbon footprint: energy sector
The energy sector is one of the main contributors to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, due to the massive combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. These energy sources generate a significant portion of global co2, thus contributing to global warming.
The transition to renewable energy, such as solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass, is a solution to reduce the carbon footprint of the sector. These technologies produce little or no GHG emissions, but their large-scale use is still ongoing.
Despite significant progress in many countries, challenges remain, such as the intermittency of renewable energy, infrastructure needs, and financing the transition. Complete decarbonization of energy requires massive investments and strong political will to achieve global climate goals.
Carbon footprint: transportation sector
The transportation sector is responsible for about 16% of global greenhouse gas emissions, mainly due to the use of fossil fuels in road, air, and maritime transport. Road transport is the main source, followed by aviation and maritime transport, both of which are growing rapidly.
Several solutions exist to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation: electric vehicles, which reduce direct emissions, and biofuels and hydrogen, which are still in development.
Public policies play a key role in reducing the sector’s carbon footprint by supporting the transition with subsidies or creating infrastructure for electric vehicles. Technological innovations, such as long-lasting batteries and alternative fuels, help accelerate this transformation, making more sustainable mobility possible on a global scale.
Carbon footprint: industrial sector
The industrial sector is responsible for about 21% of global greenhouse gas emissions, mainly due to heavy industries such as steel, cement, and chemical production. These industries require enormous amounts of energy, often derived from fossil fuels, contributing to massive co2 emissions.
To reduce the carbon footprint of this sector, optimizing energy efficiency is essential. Carbon capture and storage (CCS), for example, captures emissions before they reach the atmosphere. These technologies, though costly, offer solutions to significantly reduce emissions in the most polluting industries.
The circular economy also plays a key role by minimizing waste and encouraging material reuse, which reduces the demand for new resources and lowers emissions related to production.
Carbon footprint: agricultural sector
The agricultural sector is responsible for about 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions, mainly due to methane (ch4) production from livestock and the use of fertilizers, which release nitrous oxide (n2o). Intensive livestock farming, in particular, contributes significantly to these emissions.
Several strategies can help reduce the sector’s carbon footprint. Agroecology, which encourages environmentally friendly farming practices, and sustainable agriculture, promoting biodiversity and reducing chemical inputs, are effective solutions. Adopting a more plant-based diet also helps reduce emissions related to intensive livestock farming.
Carbon footprint: building sector
The building sector is responsible for about 6% of global greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions come from direct sources, such as gas heating and air conditioning systems, as well as indirect emissions related to electricity production for lighting and appliances.
Several solutions are available to reduce the carbon footprint of buildings. Low-energy buildings (BBC), designed to minimize energy needs, and energy-efficient renovation of existing buildings help limit the carbon footprint.
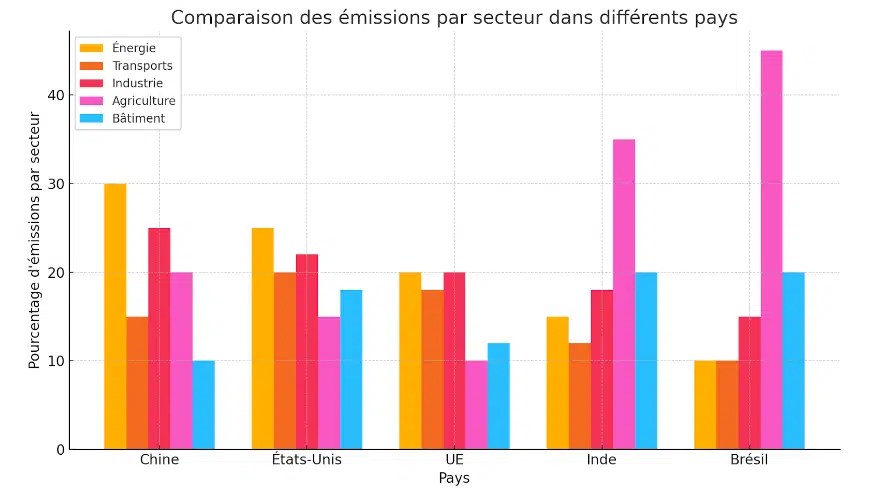
Comparison of emissions by sector in different countries
The ranking of countries by sectoral carbon footprint varies depending on the importance of each sector. For example, china and the united states have high emissions in the energy sector, while agriculture is a major contributor in brazil and india. National climate policies greatly influence emission reductions in each sector, with incentive or regulatory measures promoting energy efficiency and the transition to renewable energy.